Cosmetics raw material
Description
Henna pure is a colouring agent and active ingredient for cosmetics. It can also be used as a dyeing plant for dyeing wool, silk and cotton.
Use
In small quantities it is used as an active ingredient, for example in soap or shampoo. With solid products or pastes, the use is simple: stir until everything is well distributed. Processing is difficult in liquid products: henna pure dissolves only partly in water and partly in oil. Therefore, you will have to shake before use.
Alternatively, you can make an extract in alcohol, vegetable oil or another suitable solvent. Water cannot be used: the mixture will spoil quickly. You can simply add it to a solvent, shake every now and then and filter after some time (at least a month). The extract will mix with liquids.
Colour
In its pure state, it can be used to dye skin or hair. Mix it with water and put this paste over the part of the skin or hair to be dyed. The longer it stays on the better. Rinse it away eventually. There are hundreds of recipes with additives such as lemon, sugar or tea. It can be wrapped in plastic wrap or cloths. Whether this works better or not can only be found out by experiment. The original hair / skin colour determines the end result, this varies from bright orange to red-brown.
To make drawings on the skin it is necessary to rub the powder with water for a long time and thicken this water with, for example, glycerine or sugar.
It dyes fibres such as wool, silk and cotton, but requires a stain in most cases. The colour can vary from yellow tones through orange and red to red-brown.
Properties
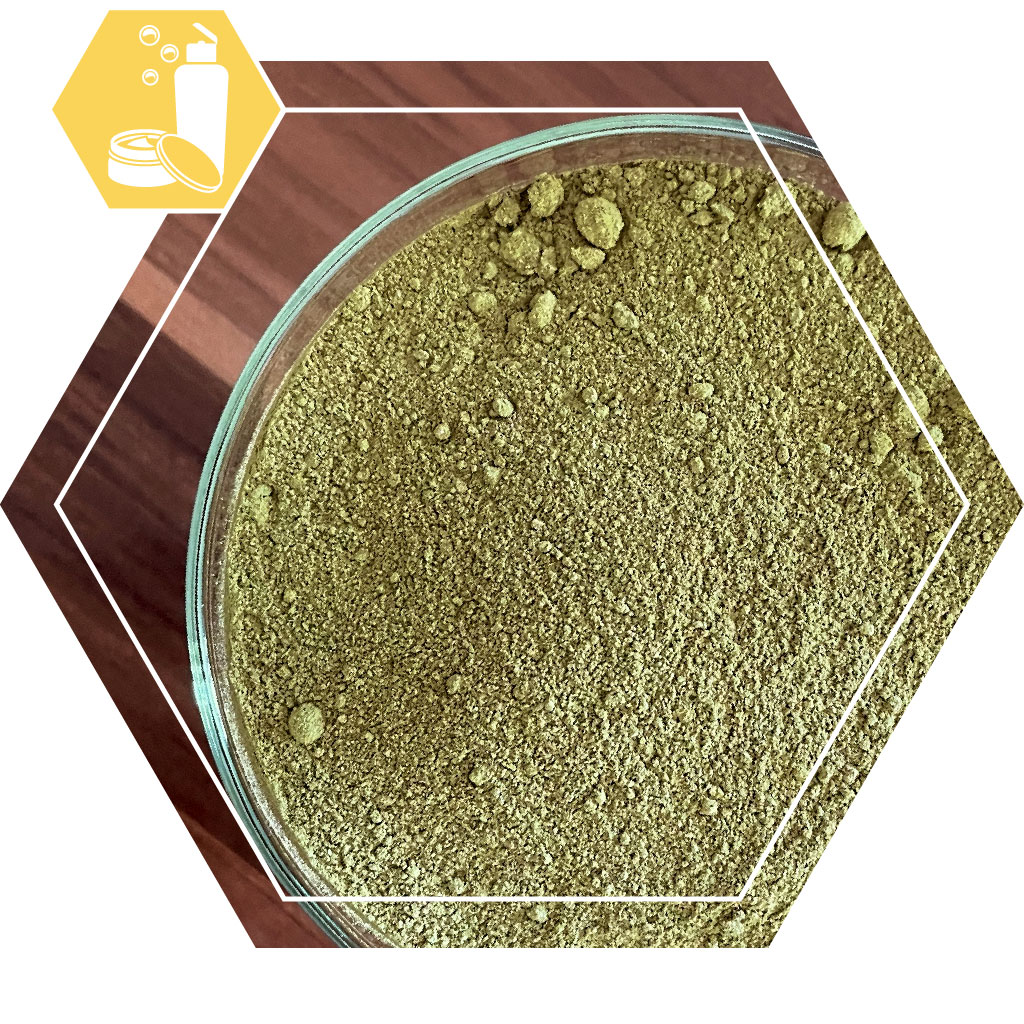
Henna pure is a moss green powder, made from ground plant parts (especially the leaves) of the henna, or Lawsonia inermis L. Our henna comes from Iran or Egypt (can vary per batch).
Henna contains the substance lawson, or 2-hydroxy-1,4-naphthaquinone. It is this substance that, due to a reaction with proteins from skin, hair or fibres, causes the discoloration.
Always remember that it can also paint unwantedly, for example the hands, clothes or wooden floor on which it has been spilled. These stains can often no longer be removed. They eventually wear out from the skin, hair grows out, but clothes, floors and many other things remain coloured.
Pure
We added the addition ‘pure’ purely for one reason. Many products are sold as henna, although it is not henna, but a product that at best consists partly of henna. This is in itself not a disaster, were it not that many of those additions are not so good for the skin. A notorious addition to so-called "black henna" is p-phenylenediamine, a synthetic dye that can cause a serious allergic reaction. Henna shampoos and colourings from European suppliers are generally safe, but contain little or no henna. Unfortunately, cosmetics from countries such as China and India do not always meet the legal requirements, and can be unsafe.
Search
We had to search for a long time for pure henna; there is also a lot of impure henna available in the European herbal trade. That is partly due to lack of interest in the product. There are several herbal wholesalers who are not interested in such quality aspects: if it looks good and smells good, they like it. The consumer is also guilty, wanting a natural product, but it has to be black instead of orange-red, liquid instead of solid, and it shouldn't cost anything. To make a good skin paint from pure henna you have to do a lot of work, synthetic substitutes work more refined and give a better result.
In this way, a lot of unclear junk has come onto the market over time. That is why we have invested a lot of time and energy in this. By the way: our supplier also sells many mixtures of henna with other things, nothing wrong with that, as long as it is clear that it is not pure.
Durability
Henna is made by partially harvesting henna plants. The plant grows well in warm dry areas. The cultivation can therefore be sustainable. The plant must be transported from the harvesting areas to Europe.
Packaging
We pack henna neatly in white plastic jars (PP).
Hazards
As ground plant parts, henna purely does not fall under the REACH / CLP legislation. A small warning is in place: henna naturally contains 2-hydroxy-1,4-naphthaquinone. This substance can be irritating. This is not very relevant given the low concentration, but we also recommend that you handle this substance with care.
Codes
Article number: 10752
INCI: Henna.